martes 27 de octubre de 2009
THE PROCESS OF NUTRITION
the animal kingdom is so huge and varied that it is very difficult to summarise how the different processes are carried out.
All animals need take food from their environment, all animals need to process the food in order to extract the nutrition elements. The processing of food takes place in the digestive system. Animal digestive system iis made up of a length of tube whish the food runs throught and in whish the food is transformed. Birds and mammals have a more complex digestive system than invertebrates whose system is much more simple or even not-exist, as in the case of sponges.
Animals also need to take oxygen from their environment, animals have a variety of differents respirator organs fish and many aquatic invertebretes have gills, insects have small tubes called trachea, and amphibeans, reptiles and mammals have lungs.
- all animals need a system for transporting the substances they need to survive to the cells this is called circulatory sistem its more conplicate in the vertebretes than that of invertebrates.
- finally all animals have an excretory system whish clean the blood and eliminates waste products.
VERTEBRATES AND INVERTEBRATES
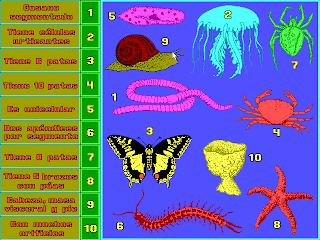
INVERTEBRATES
Poriferan: are sea sponges
Coelenterates: are jelly fish,
corals and sea anemones.
Their bodies are soft and
almost see-through.
Arthropods: are insects,
spiders, crabs and centipedes.
They have a shell, legs and
antennae. Some of them also
have wings.
Molluscs: include snails, clams,
octopus and squid. They have
soft bodies but most of them
also have a shell.
Equinoderms: include sea urchins
and starfish. They have spines
and layers whish form a hard shell.
VERTEBRATES
fish: are acuatic, vertebrates
with scales, fins and tube.like
bodies. The are oviparous
and they breathe through.
Amphibians: include frogs
and salamanders. They are
oviparus. During their early stage
of growth they are aquatic
and their breathe through
gills. The adult animal
breathe using lungs and are
ussualy land creatures.
Reptiles: include snakes,
lizards, tortoises and
crocodiles. Most of htem
are land creatures. They
have scales, they are oviparous
and they breathe using lungs.
Bird: are land creatures.
Their bodies are covered in feathers.
They fly using wings. They are
oviparous and they breathe using lungs.
Mammals: are land creatures although some of them live in the water. Most of the have hair. They are viviparous and they breathe using lungs.
divercity of plants
THE DIVERSITY OF PLANTS
The plant kingdom is the second largest kingdom ( has the most species) after the animal kingdom. There are around 200,000 known species of plant.
We have seen a non-scientific classification of plants according to their shape. In order to classify them scientifically we have to use the criteria.
Plants are either vascular or non-vascular. This means that they either have or don't have a tube like structure which transports water, nutrients and mineral salts up the steams.
Some plants produce flowers and some do not.
some plants produce fruit and others do not.
Using these three criteria we can divide the plant kingdom into four large groups:
1.Bryophytes or mosses: commonly called mosses and liverworts, they are the smallest and simplest of all the plants. They have no fruit and are non-vascular. They depend on the presence of water of their survival and life in damp places.
2.Pterydophyta: this is a group of ferns. They are medium-sized vascular plants but they have no flower or fruit. They have large leaves are divided up into different sections. They also live and damp places.
3.Gymnosperms: this plants are vascular and they have flowers but not fruit. Most of them are threes or bushes like the pine tree and juniper bush or cypress. The largest tress in the world, the sequoias, belong to this group.
4.Angiosperms: these-plants are vascular, they have flower and fruit. This group of plants is the most varied because it includes grasses, bushes and trees. Some examples are, poppies, roses, rock-rose, thyme, holm cak, chestnut etc.
NUTRITION IN PLANT
FOOD FOR PLANTS
plants are producers which means that they produce their own food. In order to do this they need to absorb substances from the soil and the air and to transform them. This process has the following steps
1.plants absorb water and mineral salts from the soil plants need to absorb to their root . Various different mineral salts are dissolve in the water. The mixture of mineral salt and water which is up sort, by the plant is noun us raw sap.
2.The steamtransport the raw sap of the leaves, the rous sap moves up wards from the roots to the steam. After these if caries on up words through the vanes in ther steen, until it riches the leaves.
3.The raw up is transformed in the leabes, the fundamental proces of nutrition takes places in the leaves. This proces is called photosintesis.
4.The elaborated sap is distributed throughtout the plant finaly the nutrients containet in the elaborated sap are distributed throughtout the plant. It richers all the cells throught the vessels.
PLANTS RESPIRATION
plants breathe just as animals do. Their leaves takes oxygen from the airand release carbon dioxyde . Howeber, during the proces of photosintesis they take in carbon dioxide and realice oxygen. This proces of respiration involbes the taking and the relasing of glases bat in the reverse order as happends during nutrition. During the proces of nutrition the plant takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen.
During the day time the two proceses, respiration and nutririon are simultaneous. Howeber at night they are not.
.
During the day time plants breathe and carry out the proces of photosisntesis at night plants do not photosintesi but they do beathe
SEAS AND OCEANS
the water in the seas and oceans covers almost three cuarters of the earthest surface earth the averal depth of the oceans is three thousand seven hundred
ninty five metres.
THE SALINITY OF SEA WATER
sea water is different from the continental fresh water in sow far as it has a wite content of south solution. the most common sauth in the sea water is
solt you lorate common south. there are also matter cuantities of lorate and others salt content of sea water ofr sea water is could it salinity and it is measere
in grams of soath lost a kg of water, the averech salinity of the water inthe oceans is 35 gramss, pear kg of water.*
in one water seas, were the water evaporate more the risajair level of salinity pearrit, in the red sea for example the salinity 41 grams pear kg of water*
in the very cold seas level of salinity is mach lower for example, in the valtic sea the salinity is only tell wgrams of sauth 10 kg of water, this level of salinity
is similar to some rivers and laker saltiest sea of all, is the dead sea whish has a salinity of 360 grams of salt pear kg of water,
haw ever the dead sea is not realy asi, it is a lake.
the constant movement of water
whe we amalise the movement of water we can see trhree differents site of movements:
1 the waves: are surface and dulations of the sea water and they are do to the action of the wind.
2 the tides: are increces and dicreaces in the level of the sea whish happend to a wrater or laced the wree or true the day.
3 the sea currents: are movements of hiuch mases of water from one point in the planet two anoter. there are one and could currents depending all the point of sorrilling of the movement and the areas
that the currents move thrue.
tarea: cuales son las corrientes marinas, y poner foto
PLANTS
what is a plant?
its a living being
the plant kingdom in made up of organims with the following common characterisc:
they have eucaryotic cells organized into tissues. each tissue has a different funtion: growth, protection, etc. in turn the
fissues are grouped together to make organs such as leaves.
they are producers. they do not need to take in food like animals because they produce their own food.
what do all plants have in common ?
all plants have roots, steams and leaves.
they are green due to substance called chlorophy
plants cannot move themselves from one place to another but they do move.
homework: investigate and write the characteristics of:
grasses: have soft, flexible, green steems sam it samples of glases are:
wheat, nettles, violets, and poppis. Many plants in this category are very small bat others like the banana plants measure of the 2 meters and look like threes
bushes: are plants with a heart, woudy steem called a trunk. Bushes have a short trunk anf the branches grow outwards from the base, very close to the ground. Some bushes are very small like thime and others can grow up 2 m tall like box.
trees: have a much longer trunk and their ranches grow higher at the plant up the trunk. Some examples of threes are:
oack
holk
hold and pain.
PLANT REPRODUCTION
plant can reproduce in two different ways:
1)asexual reproduction: only one individual is involved in creating a new plant from its own parts. When we take a cutting off a geranium and replant it we are, in fact, aiding the plant in a asexual reproducction.
2)Sexual reproducction: two individuals are involved. The uniun of special cells from each of them produces a new plant. This is what happens when plants are reproduce throught flowers. Whithing these two broad groups there are many arieties. Some of the ways that angiosperms reproduce.
3)Flowers: the reprductive organims of angiosperms and gymnosperms are the flowers have two parts:
4)the reproductive: parts of a flower are the stamen and stigma
5)the productive: parts of flower are the petals whish make up corolla and the sepals whish up calyx
6)the ovules: are inside the stigma. When the ovules come into contact with the pollen produced in the stament they turn into seed. The flowers turn into fruit.
7)The reproducction proces:
1) pollination: pollen is transported from one flower to another on the wind or by insects like bees and buterflies. This transportation is pollination.
2) the fertilisation of the ovules: when a grain of pollen reaches the ovules. This is how the ovules are ferlilised.
3) the forming of fruit: after this the flower changes. The corolla and the calyx dry up and the stigma grows and changes until it becames the fruit the seeds. Whish are formed from the ovules are inside the fruit.
4) the germination of seeds. The seeds fall on the ground and, in a very short time, they germinate. The seeds open, a samall root comes out and tiny leaves begin to grow. A new plants graws the seeds.















